Sharing Effective Lobster Farming Techniques
1. Selecting the Right Lobster Farming Location
The location must have access to a reliable saltwater source with stable salinity levels throughout the year, ideally between 30-35‰. It’s crucial that the water is free of harmful chemicals and industrial waste.
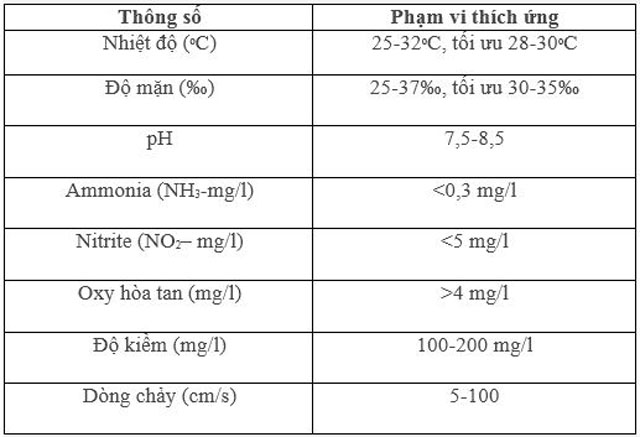
Key Environmental Conditions for Lobsters
2. Designing the Lobster Pond
- The lobster pond should be designed as a raised circular tank with a diameter of approximately 6-8 meters, covering an area of around 100 square meters and a depth of 1.2 meters.
- A circular shape promotes high centrifugal force, with a slope of around 20-25 cm at the pond’s center to optimize waste collection.
- The tank should be located close to a saltwater source for easy water supply and replacement.
- The lobster farming system should include a culture tank, storage tank, and biofiltration tank, forming a closed-loop model that enhances efficiency.
- Water is pumped from the biofiltration tank into the storage tank at a salinity of 30-35‰. Disinfect any potential pathogens in the seawater using chlorine at a concentration of 30-40 ppm.
- Aerate strongly for 48-72 hours. After aeration, check for any remaining chlorine and neutralize with thiosulfate if needed.
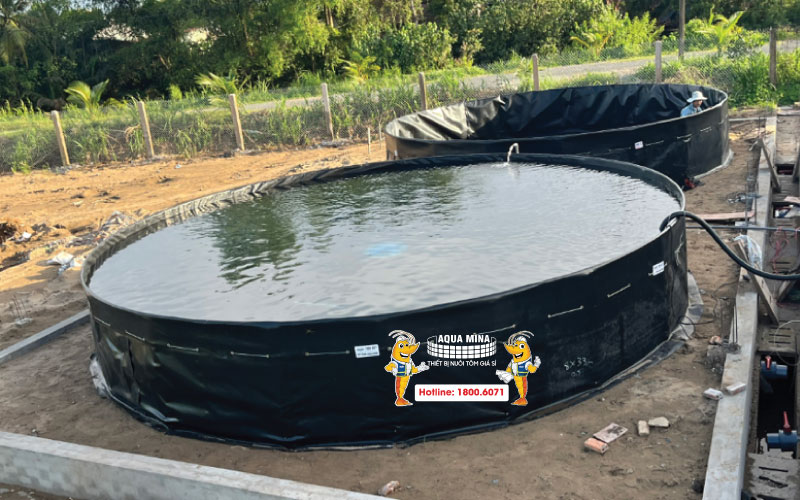

HDPE-Lined Raised Lobster Pond
3. Selecting Stock and Stocking Density
Juvenile lobsters should come from a verified source with health certificates, showing uniform size and health. The recommended stocking density is 10 juveniles per square meter.
4. Feeding and Feeding Techniques
- Industrial pellet feed for lobsters is not yet widely available, so farmers can prepare fresh feed from small fish like scad, crabs, and shellfish. Choose fresh fish, wash with saltwater, cut horizontally into 1-2 cm slices, rinse several times with fresh water, and freeze for feeding over several days.
- Feed lobsters three times daily. For the first two months, provide 20-30% of body weight in feed, then reduce to 15-20% in the following months. After feeding, remove any leftovers within 1-2 hours.
5. Proper Management and Lobster Care
- Measure environmental factors daily (water temperature, pH, dissolved O2, NH3, NO2, NO3, and H2S).
- Change water every 15-30 days, replacing 50-70% with fresh seawater, and every 60-90 days, replace 100%, clean the tank bottom, and add new water.
- Regularly monitor lobster health by observing feeding behaviors to respond promptly if issues arise.
6. Farming Duration and Harvesting
Similar to sea-based farming, lobsters raised in tanks take 18-20 months to grow. When they reach 0.7-1.3 kg, they can be harvested, either selectively or entirely, depending on size.
Contact AQUA MINA for consultation and supply of aquaculture round tanks and aquaculture equipment for high-tech shrimp farming.
- Address: 685 National Highway 1A, Binh Hung Hoa Ward, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
- Phone: 1800 6071 (Toll-free hotline)
- Email: sales@aquamina.com.vn or oversea@aquamina.com.vn
Aqua Mina's distributor in Japan:
REX INDUSTRIES CO., LTD
- Address: 1-9-3 Hishiya-Higashi, Higashi-Osaka 578-0948 JAPAN
- Email: kimakubo@rexind.co.jp
- Phone: +81-(0)72-961-9893
- Website: http://www.rexind.co.jp/e/

Ngày đăng : 29/10/2024
2947 View
Other Articles
22 kW Turbo Blower with Pneumatic Suspension vs. Suplang Blower – Which Is the Better Choice for Shrimp Ponds? Contact: 1800.6071 (Toll-free)
TURBO BLOWER FOR AQUACULTURE AND TRADITIONAL SUPLANG BLOWER – OPERATIONAL PERFORMANCE COMPARISON Hotline: 1800.6071 (Toll-free)
AQUA MINA 7.5 kW SUSPENDED AERATION BLOWER FOR AQUACULTURE – DISTINCT PERFORMANCE COMPARED TO TRADITIONAL SUPLANG BLOWERS IN SHRIMP FARMS
TURBO BLOWER – ADVANCED AERATION TECHNOLOGY THAT SAVES ENERGY COMPARED TO SUPLANG BLOWERS IN SHRIMP FARMING
15 kW TURBO BLOWER FOR AQUACULTURE – WHAT MAKES IT DIFFERENT? A COMPARISON WITH TRADITIONAL BLOWERS
Tensions in the Strait of Hormuz: Vietnam’s USD 401 Million Seafood Exports Enter a Challenging Zone
The Middle East Erupts in Tension, Import–Export Department Issues a Series of Urgent Recommendations
Benefits of Exogenous Protease in Whiteleg Shrimp Farming
Comparison of Aquaculture Turbo Blower Specifications vs Traditional Roots Blower | HOTLINE: 1800.6071
Securing an FTA with the EU: Indian shrimp puts pressure on Vietnam's market share
Indonesia’s shrimp industry recovers in late 2025 but faces tightening control risks from the United States



















.jpg)