How to Treat White Gill Disease in Red Tilapia
Understanding the Cause of White Gill Disease in Red Tilapia
The disease is caused by the filamentous bacteria Myxococcus piscicolas (from the family Myxococcaceae, order Myxococcales, class Deltaproteobacteria, phylum Proteobacteria). These bacteria thrive in pH levels of 6.5–7.5, warm temperatures of 25–35°C, and in spring and autumn seasons, especially in ponds with high organic waste pollution.
Symptoms of White Gill Disease
Gill filaments become necrotic, eroded, torn, and decayed, often accompanied by heavy mud deposits.
Hemorrhaging and erosion are visible on the surface of the operculum bones, causing deformities.
Diseased fish may exhibit abnormal behavior such as swimming sluggishly near the surface, isolating themselves from the school, and reducing or ceasing to feed.
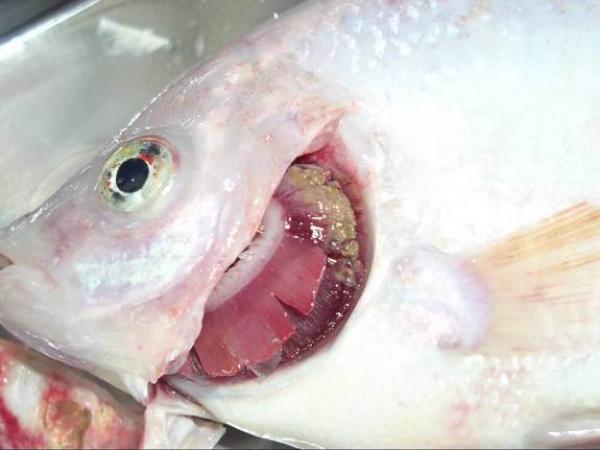
Steps to Treat White Gill Disease
Steps to Prepare and Manage the Pond for Treating White Gill Disease in Red Tilapia
Properly prepare the pond by thoroughly dredging and cleaning the pond bottom. Ideally, use lined ponds to minimize disease outbreaks.
Design an efficient siphon drainage system. During the farming process, manage the environment effectively to limit organic pollution by controlling feed quantities.
Replace pond water regularly to maintain cleanliness.
Frequently clean cage walls to ensure proper water flow rates.
Periodically treat the water with Virkon® A at a dosage of 0.7 kg per 1,000 m³ of pond water, or place it in fabric bags around the cages to eliminate harmful bacteria.
Continuously mix 5 g of Aqua C® Fish and 3 g of Grow Fish per 1 kg of feed, administering it for 7–10 days each month to enhance the fish's resistance during temperature fluctuations.
If the disease is detected early, immediately treat the fish by mixing 5–10 g of BayMet® and 5 g of Aqua C® Fish per 1 kg of feed (or 1 kg of BayMet® + 1 kg of Aqua C® Fish for 3–5 tons of fish) and feeding them for 7–10 consecutive days.
Bathe the fish in BayMet® at a concentration of 2–5 g/m³ of water.
By following these steps, farmers can effectively treat and manage white gill disease in red tilapia. Wishing you a successful and productive farming season!
Contact AQUA MINA for consultation and supply of aquaculture round tanks and aquaculture equipment for high-tech shrimp farming.
- Address: 685 National Highway 1A, Binh Hung Hoa Ward, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
- Phone: 1800 6071 (Toll-free hotline)
- Email: sales@aquamina.com.vn or oversea@aquamina.com.vn
Aqua Mina's distributor in Japan:
REX INDUSTRIES CO., LTD
- Address: 1-9-3 Hishiya-Higashi, Higashi-Osaka 578-0948 JAPAN
- Email: kimakubo@rexind.co.jp
- Phone: +81-(0)72-961-9893
- Website: http://www.rexind.co.jp/e/

Ngày đăng : 23/11/2024
2709 View
Other Articles
22 kW Turbo Blower with Pneumatic Suspension vs. Suplang Blower – Which Is the Better Choice for Shrimp Ponds? Contact: 1800.6071 (Toll-free)
TURBO BLOWER FOR AQUACULTURE AND TRADITIONAL SUPLANG BLOWER – OPERATIONAL PERFORMANCE COMPARISON Hotline: 1800.6071 (Toll-free)
AQUA MINA 7.5 kW SUSPENDED AERATION BLOWER FOR AQUACULTURE – DISTINCT PERFORMANCE COMPARED TO TRADITIONAL SUPLANG BLOWERS IN SHRIMP FARMS
TURBO BLOWER – ADVANCED AERATION TECHNOLOGY THAT SAVES ENERGY COMPARED TO SUPLANG BLOWERS IN SHRIMP FARMING
15 kW TURBO BLOWER FOR AQUACULTURE – WHAT MAKES IT DIFFERENT? A COMPARISON WITH TRADITIONAL BLOWERS
Tensions in the Strait of Hormuz: Vietnam’s USD 401 Million Seafood Exports Enter a Challenging Zone
The Middle East Erupts in Tension, Import–Export Department Issues a Series of Urgent Recommendations
Benefits of Exogenous Protease in Whiteleg Shrimp Farming
Comparison of Aquaculture Turbo Blower Specifications vs Traditional Roots Blower | HOTLINE: 1800.6071
Securing an FTA with the EU: Indian shrimp puts pressure on Vietnam's market share
Indonesia’s shrimp industry recovers in late 2025 but faces tightening control risks from the United States



















.jpg)